How IP Camera Image Stabilization Works

Have you ever tried to take a snapshot of something that’s far away? When you are using a long distance lens (higher focal point), you probably found it hard to keep the camera steady.
The higher the focal length of the lens, the more difficult it is to stabilize the image. This problem is especially significant with very long-range IP camera. When a surveillance camera is mounted on a swaying pole, or on a ship at sea, movement can affect the quality of the video. Image stabilization is used in IP cameras to reduce the effects of this motion.
This article describes the various mechanisms used to stabilize an IP surveillance camera.
In general, the method used to stabilize the video depends on the range of camera motion expected and the vibration frequency. The diagram shows how a small change in angle results in more movement the further away the field of view is.
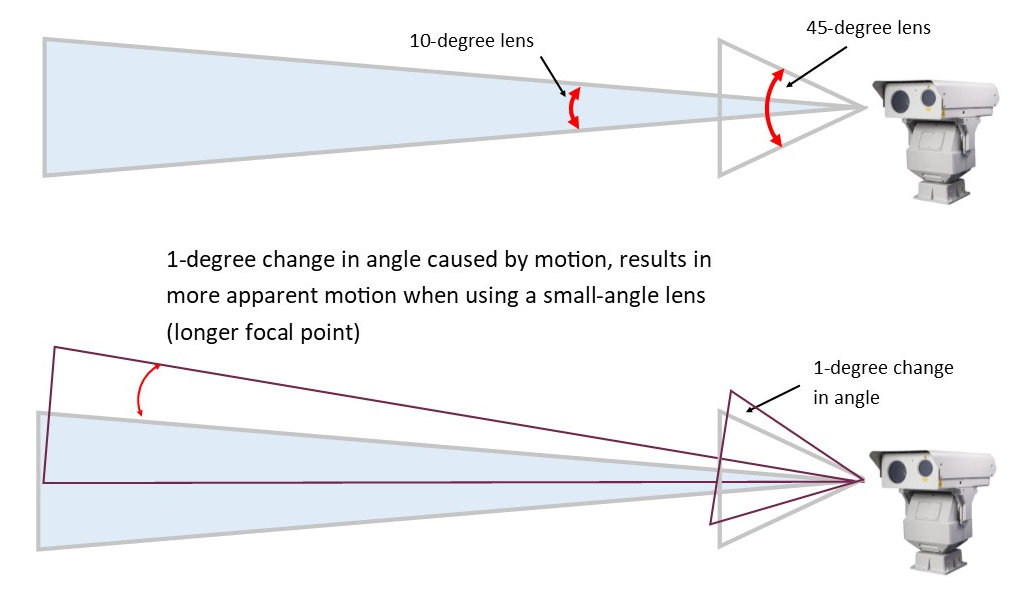
The example compares a camera with 10-degree lens to another camera with a 45-degree lens. If both cameras rotate 1-degree, the camera with the 45-degree lens, changes the field of view by 1/45 (= 2% of the field of view), while the 10-degree camera moves the field of view by 1/10 (= 10% of the field of view). The very long range cameras use very long lenses with focal lengths greater than 2000m. The very small angles of less than 1 degree, require a high degree of stabilization.
There are a number of different ways to provide stabilization. Optical image stabilization moves the lens or the sensor to compensate for angular tilt and pan motion. Electronic digital image stabilization shifts the image from frame to frame to compensate for the movement. Active physical camera stabilization attaches the camera to a pan-tilt platform that provides the stability.
Lens-Based Stabilization
Lens-based stabilization uses one of the lens elements to stabilize the image that reaches the sensor.
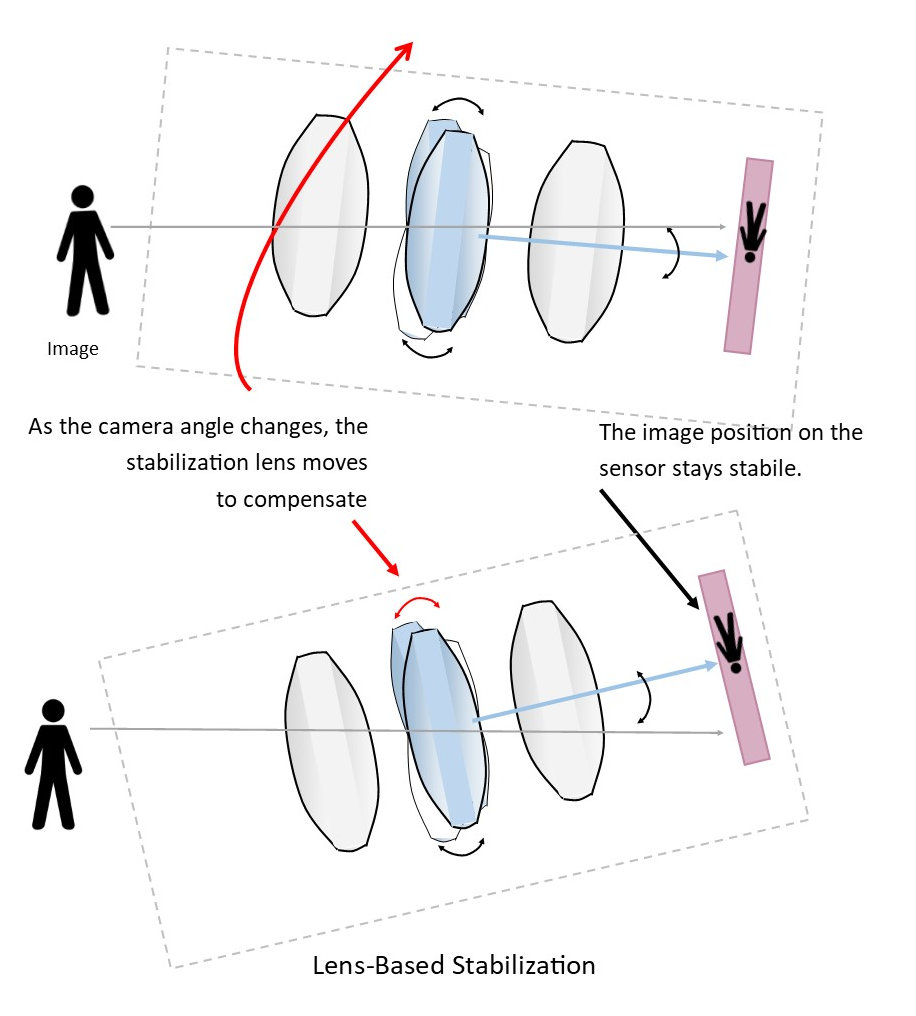
Motion is detected using an angular velocity sensor such as a piezoelectric velocity sensor (or gyroscopic sensor). One detector measures horizontal motion while the other measures the vertical movement. The lens is moved using electromagnets. This methodology provides more accurate autofocus functions than the sensor-based stabilization method, but the lens is more expensive.
Sensor-Based Stabilization
This type of stabilization moves the sensor rather than the lens to compensate for the angular motion of the camera.
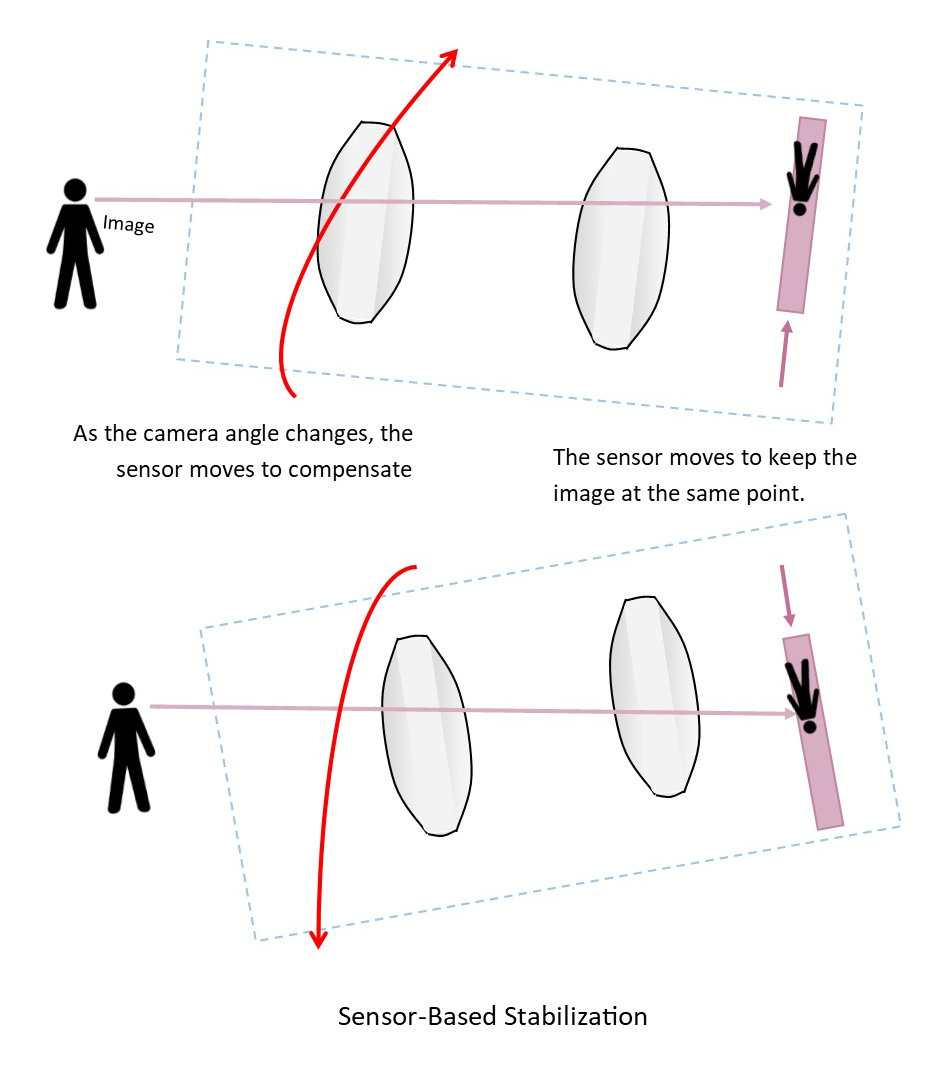
The gyroscopic detector measures the camera motion and then adjust the position of the sensor. The advantage is that you can use a less expensive lens (one without the built-in stabilization). This method provides less motion correction than the optical lens stabilization so is not the best technique for very long distance (large focal length) lenses.
Digital Image-Based Stabilization
Electronic image stabilization is used in many of the high-performance dome PTZ IP cameras. It is helpful when the camera is mounted on a pole where the wind can cause camera vibration.
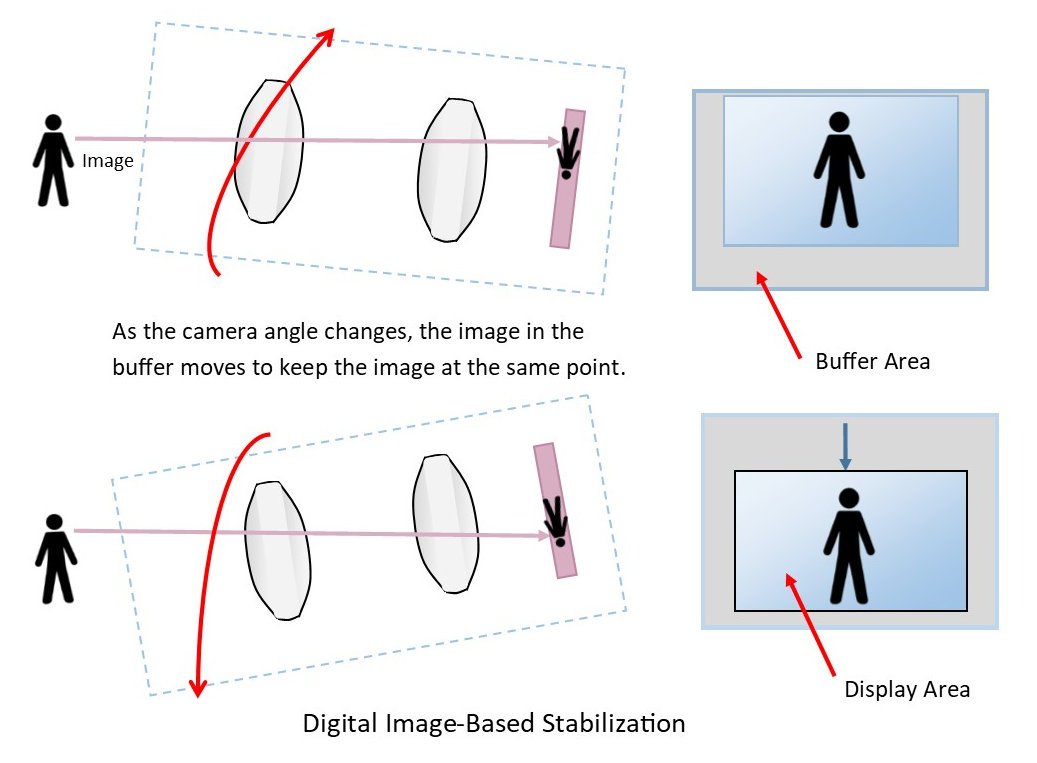
The technique tracks the image from frame to frame. It adjusts the relative position of the total image to compensate for motion. This methodology can reduce the size of the image because it uses pixels along the border of the picture as a buffer region for adjusting the picture.
Hikvision includes digital image stabilization in many of their new PTZ cameras. The Hanwha X-series IP cameras use digital image stabilization along with a gyroscopic sensor. This combination of technology improves the stabilization.

Active Camera Stabilizer
In some cases, the motion of camera system is more than the internal camera stabilization can handle. For example, if the IP camera is mounted on a moving vehicle or ship at sea. An active stabilization platform is used in this case. The video camera is attached to a pan-tilt platform that provides the stabilization. The system uses a gyro and special processing circuits to keep the camera pointed at the target.
It works well in situations where the motion frequency is very low (around 1 Hz). This type of stabilizer can maintain a target of interest on swaying poles, or on boats. It can maintain a target with up to 10-degrees of motion.
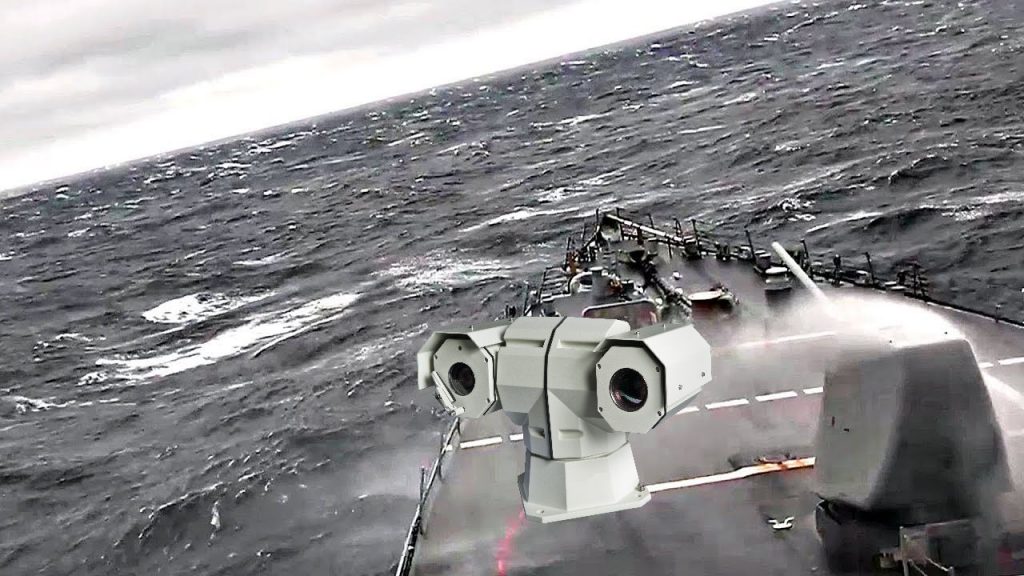

It can also be used to stabilize a camera system on a vehicle where there are low-frequency motion disturbances. But, it doesn’t work when the vehicle is bouncing around on very rough terrain.
Active gyro stabilization detects movements of the camera head. When the gyroscope detects movement, it moves the pan-tilt mechanism to compensate for the camera motion. The performance is dependent on the accuracy of the gyro sensor, the latency of the system, and the speed and precision of the pan-tilt motors.
Summary
IP cameras can be stabilized so they can be used on unstable platforms. A stable video stream can be achieved using a gyro-controlled lens, or sensor, or using digital image stabilization. A long-range camera system can be stabilized by mounting it on an active platform that adjusts the pan and tilt of the camera assembly. This provides better stabilization when the camera is on a ship at sea, or on a moving vehicle. Image stabilization is usually found on the very long-range cameras.
If you need help selecting the right IP camera and stabilization, please contact us at 1-800-431-1658 in the USA, or at 914-944-3425 everywhere else, or use our contact form.