AI Servers to IP Cameras, Access Control, and IP Paging: Power is Critical

We benefit from AI-enhanced camera systems that quickly warn us of dangerous situations. We sometimes forget that power is the lifeblood of modern computing systems. Whether it’s a single computer on a desk or a massive server farm running cloud services and artificial intelligence (AI) workloads, power keeps the digital world operating.
This article examines how Power has become a crucial factor in computer and security systems.
AC Power and Conversion to DC
One of the key factors is to provide power as efficiently as possible. The electricity that powers cities is different from the power required for computers and other electronic devices. AC Power is used for transferring power across the country from the power plant to our homes, while DC power is required for the operation of computer equipment.
Electric utilities deliver power as alternating current (AC), which is efficient for transmission over long distances. However, computers and servers require direct current (DC) for their internal electronic components, such as CPUs, memory, and storage devices. Inside each computer or server, a power supply unit (PSU) converts incoming AC into the specific DC voltages needed—often +12V, +5V, and +3.3V rails—using a process called rectification and regulation.
In large server farms, rows of rack-mounted servers are typically powered by high-capacity power distribution units (PDUs) that manage and monitor the incoming AC, which is then converted by each server’s PSU or a centralized power supply system to provide DC power reliably. To learn more about how power supplies work, please read our article How a Power Supply Works.
Big Power Challenges with Modern AI Systems

The rapid growth of AI has driven a surge in demand for computing power. Modern AI models, particularly those used in deep learning, require massive clusters of GPUs and specialized processors that consume far more energy than traditional workloads. A single high-performance server can draw several kilowatts, and large AI-focused data centers can consume tens or even hundreds of megawatts of power.
This enormous energy requirement creates several challenges:
- Infrastructure Strain: Data centers must be equipped with robust electrical systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and backup generators to ensure continuous operation, as even brief outages can cause significant disruptions.
- Heat and Cooling: High power consumption generates significant heat. Cooling systems, whether air-based or advanced liquid cooling, consume additional energy and increase the overall environmental footprint.
- Environmental Impact: The electricity consumed by server farms often comes from fossil fuel sources, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. This has led to concerns about the carbon footprint of large-scale AI and cloud services.
Moving Toward Sustainable Power

In response, many technology companies are investing in renewable energy sources, such as nuclear, solar, and wind, to power their data centers.
Power for IP Cameras, Access Control, and Paging Systems
It used to be that all the security equipment was powered by small AC/DC adapters or power supplies. Today, most IP Cameras, Door Access Controllers, and IP Paging systems are powered using Power over Ethernet (PoE). This simplifies installation and reduces costs.
What is PoE?
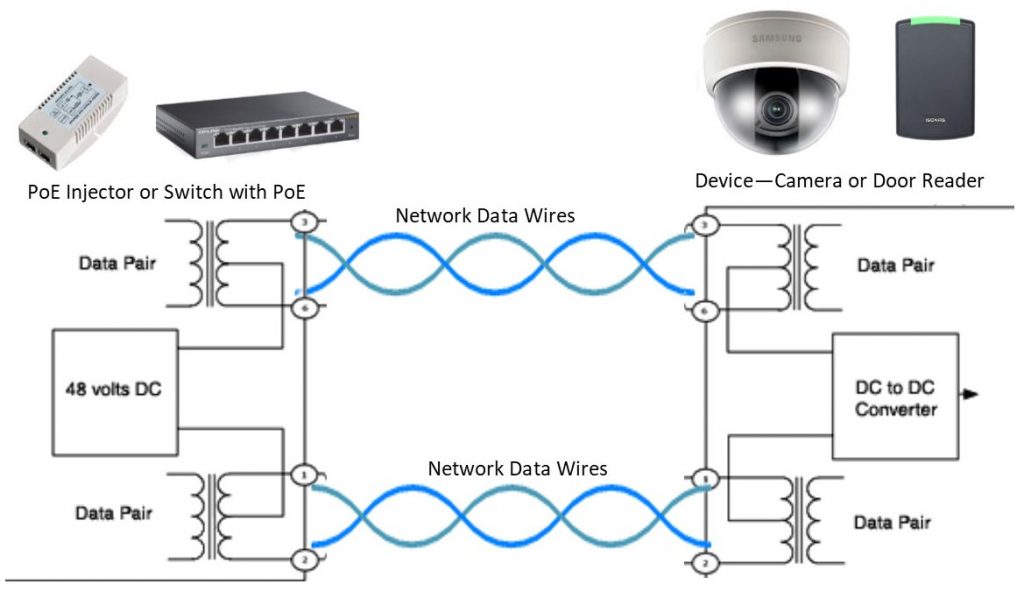
Power over Ethernet allows network cables (standard Cat5e, Cat6, or higher) to carry both data and power over a single cable. This eliminates the need for separate electrical wiring or nearby power outlets at each device location, which is especially valuable in installations where running additional AC power would be difficult, expensive, or aesthetically undesirable.
How It Works
PoE is defined by IEEE standards (e.g., 802.3af, 802.3at, and 802.3bt) and uses network switches or mid-span PoE injectors to deliver DC power along with Ethernet data signals. The switch or injector supplies power through specific wire pairs in the Ethernet cable, while compatible devices, such as IP cameras, door controllers, or paging speakers, draw the power they need directly from the network cable.
Examples of Devices Using PoE
IP Cameras: Surveillance cameras with PoE (Power over Ethernet) capability can be mounted on ceilings, walls, or outdoor poles without requiring AC power at each location. This simplifies placement and enhances security coverage.
Door Access Control Readers: Many IP-based door readers and controllers support PoE, allowing both communication with the access control server and power supply over a single cable to each entry point.
IP Paging Systems: Network-connected paging speakers (for announcements or emergency alerts) can utilize PoE for easy installation in ceilings or walls throughout a building, with a single cable carrying both networked audio data and DC power. To learn more, please read our article, How the IP Powered Speakers and Intercoms Work.
Benefits of PoE
- Simplified Installation: One cable for both power and data reduces labor, materials, and installation time. PoE can be supplied by a single power injector that adds power to an existing network cable or by a network switch that includes PoE.
- Flexibility: Devices can be installed in locations without existing power outlets.
- Safety and Reliability: PoE utilizes low-voltage DC power through the network, reducing the number of connectors and cables required. It simplifies installation wiring and enables centralized power backup with uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) connected to the PoE switch.
- Scalability: Expanding a system is easier—just run an Ethernet cable from the switch to the new device location.
Conclusion
The conversion of AC power to DC is a fundamental process enabling every computer and server to operate. As AI computing scales up, so do the challenges of managing power efficiently and sustainably. Addressing these issues is critical to ensuring that our growing digital infrastructure does not come at the expense of our planet.
PoE is a game-changing technology for modern security and communication systems, streamlining deployment and enhancing flexibility while ensuring reliable power delivery to critical devices, such as IP cameras, access control readers, and paging speakers.
If you need assistance with powering your security system, please call us at 914-944-3425, visit our website at www.kintronics.com, or use our contact form.