The Pros and Cons of Credentials used in Door Access Control

Door Access Control has come a long way, from the wooden lock and key used over 6,000 years ago to the latest biometric and mobile credentials. The advancement in access control has provided increased door security and safety.
This article summarizes the credentials used in today’s door access control systems.
A credential, such as a card or keyfob, provides a unique embedded ID that allows entry to a building with a door access control system. The door access management software maintains the list of users and their credentials. The credential can be a card, keyfob, smartphone, or a more secure system using a biometric credential. In all cases, the ID from the credential is sent to the controller or computer. If the ID matches one of the people in the access control management system, it will unlock the door.
History of Door Access Credentials
The first type of card reader used a Wiegand-type connection developed in the 1980s by John Wiegand. The Wiegand effect card readers detected wires embedded in cards that provided the ID.
Magnetic-type cards use a magnetic material similar to conventional magnetic audio tape. The magnetic stripe on the card held the ID that the door reader read. This technique had the advantage of changing the code, but the disadvantage was that it wore out over time and was easy to copy. It provided a relatively low level of security.
Current Door Reader Credentials
There are several types of credentials used in door access control systems. Many proximity cards use RFID (Radio Frequency ID) for communication.
Proximity (or Prox) Cards
Proximity cards use a contactless technology made from PVC material. There are several types of Prox (or contactless) cards. This same technology is also used in keyfobs and tags. The first type used 125 KHz to transfer information. The more recent type of card use 13.56 MHz for communication. The 13.56 MHz cards are called “Smart Cards” because they provide storage, increased capability, and better security.
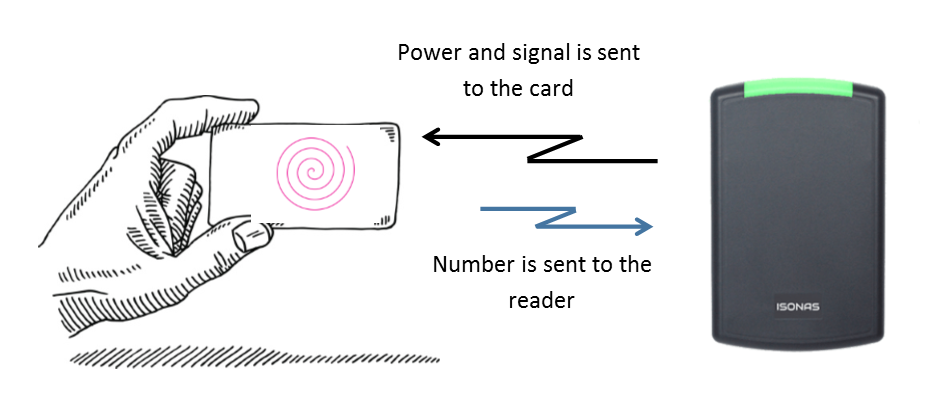
Prox cards or RF Cards use an embedded tuned antenna and amplifier that converts the signal from the door reader into power that runs the integrated circuit. The ID is held in the card’s circuits. When it receives a signal from the reader, it replies with its ID.
Smart Cards
A Smart Card uses 13.56MHz for communication and contains memory. Mifare cards were the first popular smart cards. They were used in Europe for public transportation to identify and track transportation payments.
Smart cards use 128-bit code that provides a dramatic increase in the number of unique card IDs available as well as encryption. HID provides advanced DESFire EV3 + iClass that provides increased security.
When to Use Prox Cards
The Prox cards are the most popular type of credential. They are compatible with most door readers. Physical cards can include printed information so they can be used as an identification card.
Mobile Smartphone Credentials
Mobile credentials use your smartphone instead of a card or other credential. The smartphone provides the authorization token like a Prox card or keyfob. That’s why we call it a mobile credential.
The smartphone connects to a door reader using Bluetooth, NFC, or WiFi. Bluetooth (BLE) is the most common type of communication used in the security market.
Mobile credentials are more likely to be brought with you than a card that could be lost or forgotten at home. The smartphone is a personal device that has become a part of our daily activities. Because of its importance, it is unlikely to be given to another person.
The added security of unlocking the smartphone adds additional security against misuse.
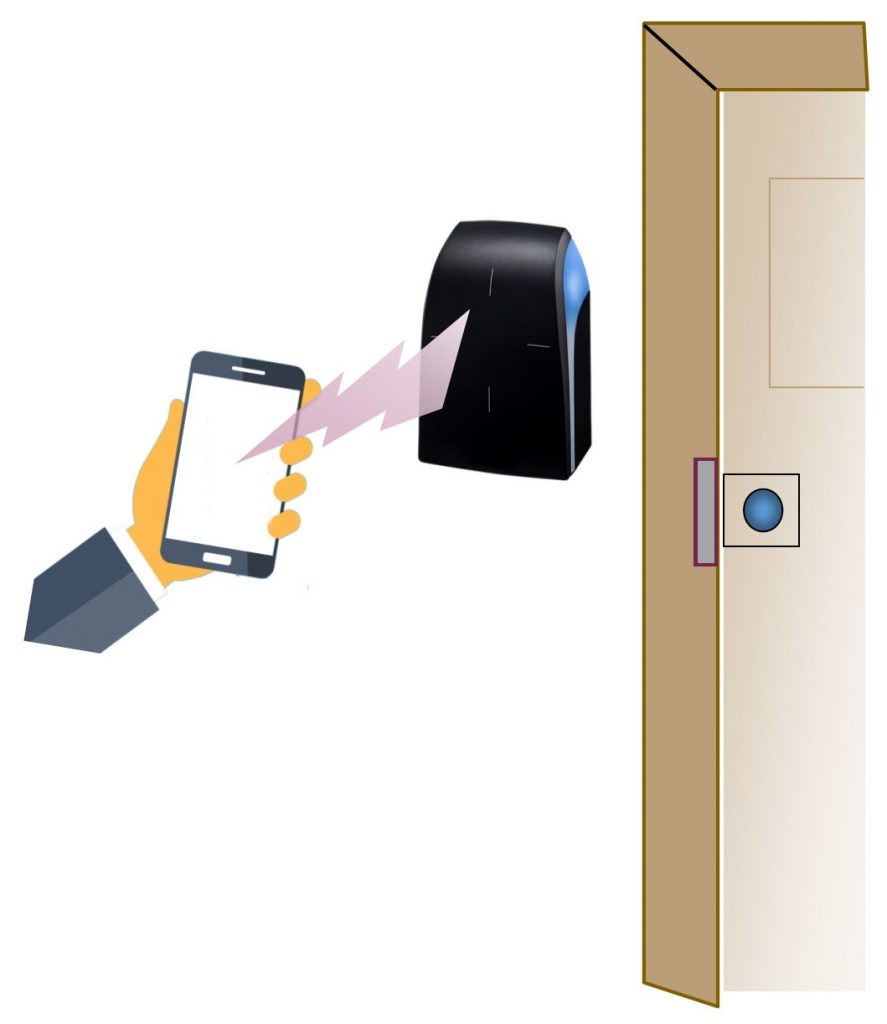
When to Use Mobile Credentials
Mobile or smartphone credentials provide enhanced security and are more convenient than a card credential. They are best used when most of the users have a smartphone. Some door readers have multi-credential support, so they can use an older card credential if a person doesn’t have a smartphone.
Biometric Credentials
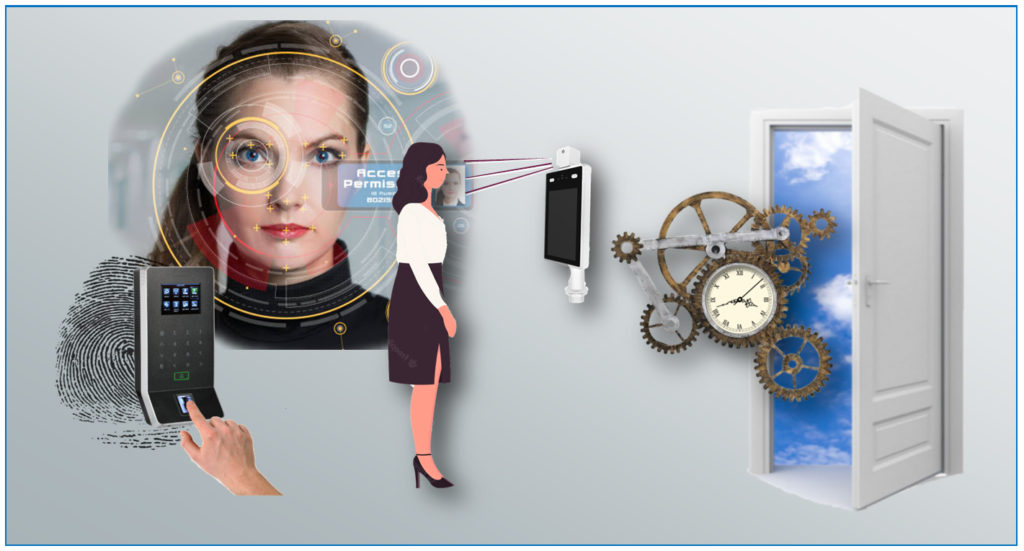

The biometric ID credential is created from a person’s physical characteristics, such as a fingerprint, palm scan, finger-vein, or facial recognition algorithm. They identify human characteristics, making them much more secure than standard card credentials. Card credentials can be stolen, lost, or given to another person.
Fingerprint Readers;
Many fingerprint readers have problems reading dry and damaged fingerprints. The new readers include advanced technology that can read these challenging fingerprints. They are also able to detect live fingers for a higher security level.
The matching and verification algorithm for finger-vein identification is more accurate than the fingerprint method but is not a touchless door entry.
Even though this is a reliable biometric reader, it is not as popular as fingerprint readers or face recognition.
Palm Readers
Palm readers are similar to face recognition readers in that they are touchless. You hold your hand over the reader, and it remotely views the pattern of wrinkles in your palm.
Face Recognition
These specialized facial recognition systems use cameras to capture the full facial image. The software uses various computer algorithms to build a definition data set, including machine learning. Facial recognition indoors is more reliable than outdoors because the changing light makes the recognition process difficult. The TVIP-Face8WP face recognition panel is one of the few outdoor devices because it has intelligence that allows operation in varying light and weather conditions.
When to Use Biometric Credentials
Biometric credentials are one of the most secure ways of identifying a person. Since you don’t have to purchase cards or even add an app to your smartphone, it is the least expensive type of credential. The door reader costs more than the card credential door reader, but the savings are balanced by not having to purchase card credentials.
Summary of Credentials for Door Access Control
The most popular type of credential is a card. Historically this was one of the first electronic types of door entry. Recent credentials are located in your smartphone. This has specific advantages over the card credential. The most secure credential is your characteristic detected by biometric door readers.
If you would like help selecting the best credential for your door access system, please get in touch with us at 1-800-431-1658 in the USA or 914-944-3425 everywhere else, or use our contact form.