CD Servers, RAID, Optical Disc or Cloud Storage? That is the question
by Dennis Gallen

“What’s the difference between a jukebox and a CD/DVD Server?” That was the question we used to get. It was a time when CD-and DVD discs were a great way to archive data. Today the there are a number of different storage options available. We continue to get questions about the best way to store data. We are asked, “What is the difference between Cloud storage and optical disc storage? And, “What is the difference between tape and optical discs”?
The answer depends on your specific application and objective. For example, one of the first things to consider is whether or not you need to archive your data or just store it for a short period. Archiving means you plan to keep it for over 25 years, while just storing it means you probably only need it for less than a year. To learn more about the difference between archiving data and storing data take a look at our article “How to Comply with the Archiving Regulations Without Paying an Arm and a Leg”.
Another thing to consider, is where you feel comfortable storing your data. You may decide that you would prefer to control your data at your own facility, or you may like the concept of using a remote storage system in the Cloud. This article provides information that will help you select the right product for your application.
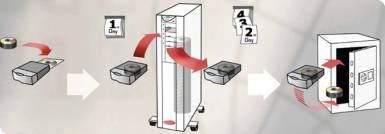
Optical Jukeboxes or Libraries for Archiving Data:
An optical jukebox is excellent for archiving data in your own facility. If you have critical data that you are concerned about leaving your location, then this is the best solution for you.
The jukebox contains multiple drives that allow you to quickly write data to discs. Jukeboxes hold from 35 to over 500 Blu-ray optical discs.
Here are the pros and cons of this type of storage:
Pros:
- They are easy to integrate within your computer system structure.
- They connect to a Windows computers and use special software to write and retrieve the data.
- Users on the network can copy or drag and drop data to the server which automatically transfers the data to an optical disc in the jukebox.
- Once data is written to the discs, it can be accessed by users on the network.
- Data caching can be used to increase access time. For example, PoINT Jukebox Managerprovides tiered storage that supports high speed hard drives for caching frequently used data. This dramatically increases the speed for retrieval of data.
- Large files and directories can be spread over multiple media using File Spanning.
- Larger jukeboxes have six or more drives, so more users can simultaneously access the different discs.
Cons:
- Jukeboxes are relatively slow when compared to hard drives or remote Cloud servers (if you have a fast Ethernet connection).
- All the jukeboxes work best when only a few users need to access the discs at the same time.
- Small jukeboxes have only one or two multi-function drives, so only one or two users can share the jukebox at the same time. If additional users want to use a new disc, they have to wait for the disc to be swapped by the robotics in the jukebox.
- It takes about 4 to 9 seconds to swap a disc.
Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is a remote set of servers and storage devices that are controlled by some other company and available on the Internet. For example, Cloud storage is provided by companies such as Amazon, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Verizon and others. These companies charge at a rate of GByte/month, so large amounts of storage can get expensive.
Pros:
- Data is accessible from any place that has an Internet connection.
- It is easy to use with desktop folders that make it very easy to store the data.
- There is usually very good disaster recovery. Cloud storage facilities usually provide redundant servers and storage that assures your data is safe.
- In some situations, Cloud storage can be cost effective. For example, besides saving money on capital equipment, you may also require less staff, and save money on power.
Cons:
- The bandwidth of your Internet connection can affect the availability and speed of storing and accessing your data, especially if you have large files.
- If you have no Internet connection, you can’t get your data
- Even though many companies try to provide assurances that your data is safe, there are some concerns about piracy of important remote data.
Tape Libraries:
The tape library is a very popular way to store data. It has been used for decades as an inexpensive off-line storage system. Today there are tape libraries that have automated the off-line storage of tape cartridges.

Pros:
- It is a low cost solution that can hold many TB of data.
- Tape has historically been less expensive than optical media.
Cons:
- Tape is not archival media.
- Tape is linear storage, so it takes a long time to randomly retrieve data from the middle of a tape reel.
- Optical media costs about the same as tape and is the better choice if you need to archive your data.
Summary
Optical storage and Cloud storage are both excellent technologies for archiving data. Cloud Storage is faster and requires less work for your IT people, but Optical storage provides better safety and security.
Need more information? Please give us a call at 1-800-431-1658 in the USA, or 914-944-3425 everywhere else. You can also contact us for more information.