IP Camera Settings for Low Light
(This article was updated to reflect new IP cameras, 10/16/2017)

When selecting cameras for your IP camera system, one of the most challenging situations is when you have very little light. When it’s dark, there can be motion smearing and amplifier noise that degrades the image.
All IP cameras handle low light by opening the lens iris, increasing amplifier gain, increasing shutter time, and switching to day/night mode. But, what is the best IP camera for low light operation, and what are the correct settings? This article provides guidelines for selecting the right camera and adjusting the image settings.
Selecting the IP Camera for Low Light Conditions
The low light sensitivity of the camera is a significant specification, but it’s not the only thing to consider. You should also select a camera that includes adjustments for amplifier gain, iris control, frame rate, and shutter speed. The camera should also have a good signal to noise ratio and include a day/night IR filter. In some applications, it can also help to select a camera with a built-in IR illuminator. (See below for more about adding light).
One thing to note is that the camera and the settings can be different depending on your specific application. For example, a camera used to see people walking close to the camera (within 50 ft.); will be different than a camera used to view a parking lot.
Camera Lens: The lens is an important factor in low light operation. The lens should have a low f-number. The lower the f-number the more light the lens can pass. When selecting a variable lens, the highest light transmission light (the lowest f-number) is when the lens is set to its widest angle. As the lens is zoomed (magnified) less light is passed through the lens. For example, a camera that has a variable focal length of 2.8 mm to 12 mm will have a variable light transmission of f1.4 (wide) to f3.6 (tele).
Some Camera Examples:
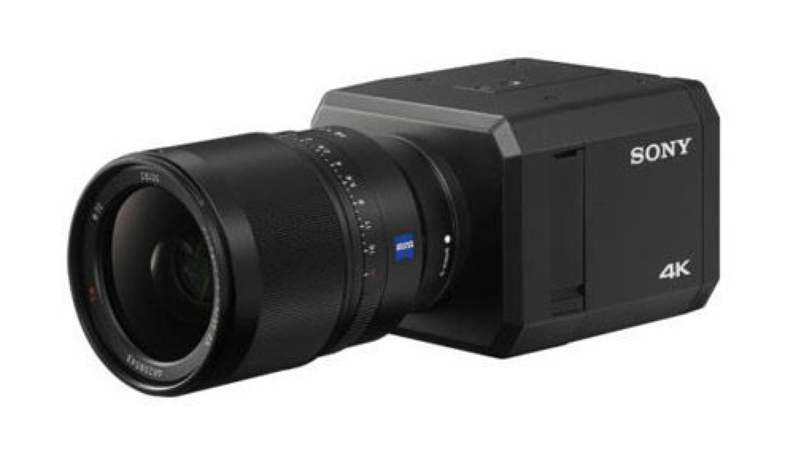

The better low-light cameras can see by the light of the full moon. This provides about 0.1lux of light. Some of the latest cameras can see with less light. In general, low light performance depends on the size of the sensor and the resolution.
The highest resolution and lowest light level camera we have tested is the Sony SNC-VB770. This amazing camera not only has very high, 4K resolution, it also has a minimum low light sensitivity of 0.007Lux (in color). It’s an expensive camera (around $7500), but at night it can see things no other 4K camera can see.
There are a number of more reasonably priced 4K IP cameras that are priced at under $1000. For example, the Hikvision 8-Megapixel dome camera, model DS-2CD4585F-IZH, specifies the low light performance at 0.014 lux @ (ƒ/1.4, AGC on). You can also consider the Hanwha PNO-9080R 4K bullet camera. This 12-Megapixel camera specifies the low light sensitivity at 0.3lux @ F1.6 in color. It includes an IR illuminator and a motorized zoom lens.
Some of the new 2-Megapixel cameras have better low light sensitivity than the higher resolution cameras. For example, the Hikvision DS-2C4526FWD-IZH IP dome camera has an amazing 0.0027 low light sensitivity.
Low Light Noise Processing
Some new cameras, such as the Hanwha X-Series, include special noise reduction technology. The processor removes noise artifacts that appear when the amplifiers are struggling to amplify the video signal.
Camera Settings
Here are some guidelines for adjusting the camera settings, but please remember you may have to experiment to get the right settings for a specific situation.
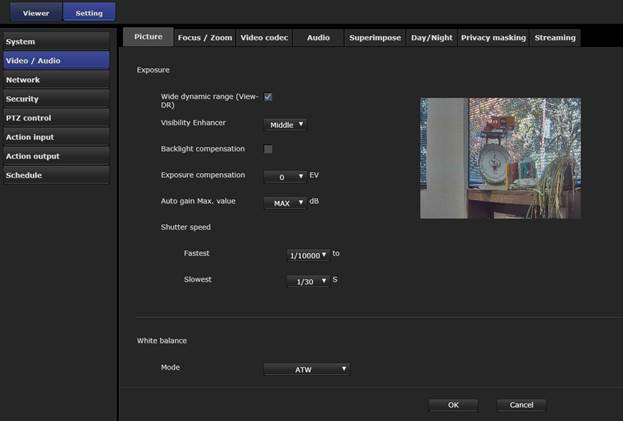
Iris: The iris controls the amount of light that hits the sensor. When there is a lot of light the iris opening is very small, and when there is very little light, the iris opens up as much as it can. In most cameras the iris setting is automatic, but in some IP cameras, you can make some fine adjustments. When you open the iris, you can get the most light on the sensor, but unfortunately, this also reduces the depth of field. The depth of field is the distance between the nearest and closest distance where objects are still in focus. When the iris is closed, the depth of field is very long, but when the iris is opened, the depth of field is very short. This means that at night, especially when you are close to the camera, the picture may not be clear.
Shutter speed (Frame Rate): The longer the shutter is opened, the more light falls on the sensor, but a long shutter period can also cause motion blurring. The shutter time is also related to the frame rate. If the frame rate of the camera is 30 fps, then the maximum shutter period is 1/30th of a second. The best shutter opening will depend on what you are viewing. If you are viewing people walking, then you can reduce the frame rate (maybe around 10 fps) and keep the shutter open longer, but if you’re viewing moving vehicles, you will need to keep the shutter time short.
Amplifier Gain: In some IP cameras you can set the amplifier gain to 50 IRE or 30 IRE. At 50 IRE the camera circuits will amplify a video signal that is 50% of the maximum value, while at 30 IRE the camera will operate with signals that are 30% of the maximum signal level. When operating at 30 IRE, there is usually quite a lot of noise seen in the video. Sometimes IP cameras use different terms to describe the amplification. For example, some of the Sony cameras provide amplifier gain in dB, while Hanwha allows the gain to be adjusted from low, medium, to high.
Day/Night Mode: The better day/night cameras have IR filters. If you plan to use the camera when it is dark, make sure the Day/Night mode is turned on. The camera will automatically switch to B/W and removes the IR filter when it gets dark.
Wide Dynamic Range: Many of the high-performance cameras include dramatically increased wide dynamic range ( over 130 dB WDR). They do this by taking multiple frames at different exposure values and then averaging the results. This excellent feature allows you to see areas where there is a large difference in the light. For example, if you are viewing a lobby with large glass windows, and you want to be able to see people inside as well as outside in the bright sunlight, WDR will allow you to do it.
The problem with this technique is that you require very fast frame rates and consequently short shutter times for this to work. This reduces the low light sensitivity of the camera. It is best to turn off WDR in low-light situations.
There’s one camera that we know of that uses a different technology to allow viewing high contrast images. The Sony EM600 and VM600 family of cameras provide an additional feature called “Visibility enhancer” technology. This adjusts the brightness and contrast of the image on a pixel by pixel basis and allows you to see everything in the view. This is not quite as good as the frame averaging technique (which Sony calls “View-Dr) technology), but it’s an excellent alternative when you have to use the camera in both daytime and low light nighttime applications.
Compression: The type of compression can determine the video quality at night. H.264 doesn’t perform when there is a lot of amplifier noise, and it uses much more bandwidth. It’s best to switch to MJPG compression.
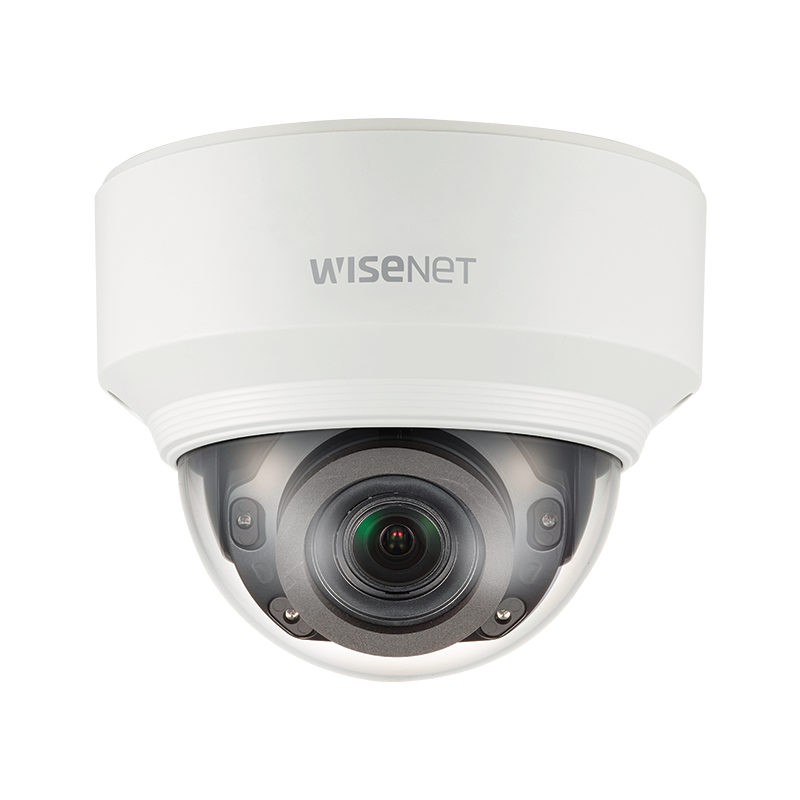

Adding Light: Some cameras are available with built-in IR illuminators. The IR-illumination range can vary from 20 m (65 ft.) to over 200 m (656 ft.) depending on the type of camera. Some of the more sophisticated PTZ cameras include IR illumination that varies depending on the zoom of the lens. It also means you will see the image in gray-scale (BW), instead of color. You can also add separate IR illumination. Separate IR lights are more powerful and have a range of over 1000 ft. (300m).
The Hanwha (Samsung) model XNV6080RV is an example of a dome camera with built-in IR. It has an IR operating range of up to 50 m (164 ft.).
If you need a surveillance IP camera system that can see at very long distances, there are some special long-range PTZ cameras with laser illumination that can see things over 5,000 m (3-miles).
The alternative to an IR-illuminator is standard white light. If there is enough light, the IP camera will stay in color mode rather than switching to B/W mode. This allows you to see the color of the vehicle. For example, if you are viewing a parking lot at night, and you add more lights, you will see everything much clearer.
Conclusion:
Higher performance IP cameras can be used to view nighttime areas. You can select the camera and then adjust the settings for the best performance. Unfortunately, the same settings don’t work in every application. You may have to experiment to get the best results for your specific environment.
If you need help selecting the right IP camera system, or in adjusting the settings, please contact us. We have a lot of experience with IP camera systems. We can be reached at 1-800-431-1658 in the USA, or 914-944-3425 (everywhere else), or use our contact form.