
Anyone who has traveled by airplane has probably gone through a walk-through metal detector. These security devices have also been used in schools, sporting events, government offices, and concerts. They are part of a total security system that includes cameras, door access control, and emergency paging systems.
Metal detectors are effective and safe. Just like IP cameras and door access control, they add to your safety and security. Here’s how they work.
The Science Behind Metal Detectors
The metal detector utilizes the laws described by a Scottish physicist named James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879). He discovered that magnetism and electricity are related. An example of the relationship is a coil of copper wire wrapped around a metal nail. When current is applied to the coil, the metal nail becomes magnetized.
When an electric pulse is sent through a coil of wire, it creates a magnetic field. When the field hits a metal object, it reflects back and can be detected using another coil of wire. The size and timing of the detected pulse is used to define the size and position of the object.
How They Work
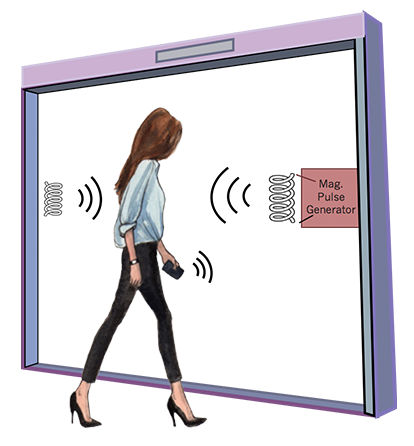
Walk-through metal detectors typically use pulse induction (PI) technology. The PI systems send powerful, short bursts (pulses) of current through the coil of wire. Each pulse generates a short magnetic field. When a piece of metal passes through the magnetic field, a reflected magnetic field is created. This magnetic field then reacts with the receiver coil, which, in turn, triggers the alarm system. This initiating spike lasts a few microseconds (millionths of a second) and causes a current to run through the coil. This subsequent current is called the reflected pulse and lasts only about 30 microseconds.
A typical PI-based metal detector sends about 100 pulses per second, but the number can vary based on the manufacturer and model, ranging from about 25 pulses per second to over 1,000.
The walk-through metal detectors create large magnetic fields that cover all of the space inside the rectangular arch of the metal detector. If a person walks through the metal detector and sets off the alarm, airport security is informed that this person could potentially be hiding a dangerous, metal-based weapon, such as a knife or a gun, and further research is conducted.
The latest metal detectors have multiple zones that not only sound an alarm but also can tell the security person where the metal object is located.

The multi-zone walk-through metal detectors contain multiple coils that create the separate detection zone. They can detect multiple objects, and display all the areas where they can be found. Systems are available with up to 33 zones. There are alarm lights on the side of the unit making it much easier for the security person to find the object. To learn more, take a look at our video about “How Walk-through Metal Detectors Work.”
Walk-Through Metal Detectors are Safe and Effective
The Health Physics Society wrote a fact sheet on airport security that said, “Even though magnetic fields [created by metal detectors] are a form of radiation, the radiation the machine emits is nonionizing … [and] does not cause biological damage. Therefore, even repeated exposure to metal detectors has no associated radiation risk.” With this in mind, airport metal detectors provide a very effective and safe method of enforcing security in airports, schools, and businesses.
Summary
Walk-through metal detectors utilize magnetic fields to detect metal that passes through them. The science behind how they work is based on Maxwell’s equations. The latest detectors include multiple detection zones allowing them to pinpoint the location of the metal causing the alarm. They have been proven to be a safe and effective method for maintaining security.
If you need help selecting the right walk-through metal detector, please contact us at 1-800-431-1658 in the USA, or at 914-944-3425 everywhere else, or just use our contact form.